In complex piping systems, the efficient and safe redirection of flow is paramount. This critical function is primarily served by the steel elbow, a fundamental pipe fitting designed to change the direction of fluid flow by various angles, most commonly 45, 90, or 180 degrees. These essential components are manufactured from a variety of materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, each selected based on the specific demands of the application, such as pressure, temperature, corrosion resistance, and fluid type. As industries evolve, the demand for high-performance elbows that offer superior durability, precise dimensions, and optimal flow characteristics continues to rise. This demand drives innovations in manufacturing processes and material science, ensuring pipeline integrity across diverse operational environments.
The choice of an appropriate steel elbow is influenced by numerous factors, including the operating pressure and temperature, the corrosive nature of the transported media, and the specific industry standards that must be adhered to. For instance, in chemical processing plants, elbows must withstand aggressive corrosive agents, while in high-pressure oil and gas pipelines, their structural integrity under immense stress is critical. Modern manufacturing techniques leverage advanced metallurgical knowledge to produce elbows that not only meet but often exceed stringent performance criteria. This technical precision ensures seamless integration into existing systems and contributes significantly to the overall efficiency and longevity of pipeline infrastructure, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs for B2B stakeholders.

The production of a high-quality steel elbow begins with the selection of premium raw materials, typically seamless or welded pipes. Common materials include Carbon Steel (ASTM A234 WPB), Stainless Steel (ASTM A403 WP304/304L, WP316/316L), and various Alloy Steels (e.g., ASTM A234 WP11, WP22, WP91). The manufacturing process generally involves several key steps to achieve the desired shape, strength, and dimensional accuracy. These methods include hot forming (mandrel bending), cold forming, and in some specialized cases, precision casting or CNC machining for complex geometries or small batches. Mandrel bending, a prevalent hot forming method, involves pushing a heated pipe over a die containing a mandrel, which shapes the pipe into the elbow form while maintaining its cross-sectional integrity.

Quality control is integrated at every stage of steel elbow production. Products undergo stringent testing to meet international standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems), ANSI B16.9 (Factory-Made Wrought Butt-welding Fittings), and ASTM material specifications. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods like ultrasonic testing (UT), radiographic testing (RT), magnetic particle testing (MT), and liquid penetrant testing (PT) are routinely performed to detect any internal or surface flaws. Hydrostatic pressure testing is also conducted to ensure leak-tightness and structural integrity under design pressure. This meticulous inspection process guarantees that each elbow delivers superior performance and a long service life, significantly reducing potential failures and associated costs in industries such as petrochemical, power generation, and water treatment.

The performance and compatibility of an elbow are defined by its technical parameters. These include Nominal Pipe Size (NPS), Schedule (wall thickness), material grade, end connections (butt-weld, socket-weld, threaded), and bending radius (long radius vs. short radius). Long radius elbows have a radius of curvature equal to 1.5 times the nominal pipe diameter (1.5D), while short radius elbows have a radius equal to the nominal pipe diameter (1.0D). The choice between these depends on space constraints and desired flow characteristics; long radius elbows offer less pressure drop and turbulence, making them preferable for critical fluid flow applications. Understanding these specifications is vital for engineers and procurement specialists to ensure optimal system performance and regulatory compliance.
| Parameter | Description | Typical Values / Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | Chemical composition and mechanical properties. | ASTM A234 WPB (Carbon Steel), ASTM A403 WP304/316 (Stainless Steel), ASTM A860 WPHY (High Yield) |
| Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) | Standardized pipe size identifier. | 1/2" to 48" (DN15 to DN1200) and above |
| Schedule (Wall Thickness) | Indicates the pipe wall thickness, affecting pressure rating. | Sch 10, Sch 40, Sch 80, Sch 160, XS, XXS |
| Bend Angle | Angle of flow direction change. | 45°, 90°, 180° (Return Bend) |
| Bend Radius | Radius of curvature relative to pipe diameter. | Long Radius (1.5D), Short Radius (1.0D), 3D, 5D, 7D, 10D (for custom bends) |
| Manufacturing Standard | Governing standards for dimensions, tolerances, and testing. | ASME B16.9, ASTM, MSS SP-43, EN 10253 |
| End Connections | Method for connecting to pipes. | Butt-weld, Socket-weld, Threaded (NPT, BSPT) |
These parameters ensure that the selected steel elbow integrates seamlessly into the pipeline system, fulfilling its role efficiently without compromising system integrity. For example, a stainless steel 180 degree elbows often sees use in heat exchangers or compact flow reversal systems where minimal space and maximum redirection are needed, while a standard 90-degree carbon steel elbow is a staple in general utility lines. Compliance with industry standards like ASME B16.9 is not merely a formality but a guarantee of interchangeability, safety, and performance, providing peace of mind to project managers and engineers.

The versatility of steel elbow fittings makes them indispensable across a multitude of industries. From the high-pressure environments of oil and gas exploration to the precise flow management in chemical and pharmaceutical facilities, elbows are the unsung heroes of fluid transfer. They are critical in petrochemical plants, power generation facilities, metallurgical operations, water treatment and supply systems, and even in shipbuilding. Their ability to manage directional changes in pipelines efficiently directly impacts system performance, reducing pressure drop and ensuring laminar flow where required. The specific advantages vary by material, but common benefits include enhanced durability, superior corrosion resistance, and high-pressure tolerance.

In an example application, a petrochemical refinery implemented stainless steel 180 degree elbows in their high-temperature steam lines. The inherent corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength of the 316L stainless steel significantly reduced the erosion and thermal stress seen with previous carbon steel fittings, leading to a 15% improvement in energy efficiency due to reduced pressure loss and a 30% extension in component lifespan. This case highlights how selecting the right steel elbow translates directly into operational savings and improved safety.

The market offers several types of steel elbow fittings, each with distinct properties and best-suited applications. Understanding the differences between common variants like carbon steel, stainless steel elbow, and galvanized steel elbow is crucial for making informed procurement decisions that balance performance, cost, and longevity. While carbon steel elbows are generally more economical and suitable for general purpose applications, stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance, and galvanized steel provides enhanced protection against rust in specific environments.
| Feature | Carbon Steel Elbow | Stainless Steel Elbow (304/316) | Galvanized Steel Elbow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Low, prone to rust without coating. | High (Excellent for various acids, alkalis). | Moderate (Zinc coating provides barrier protection). |
| Temperature Range | -20°C to 450°C (approx.) | -196°C to 870°C (approx.) | -20°C to 200°C (approx., zinc melts at higher temp). |
| Cost | Lowest | Highest | Medium |
| Strength/Durability | High, good mechanical properties. | Very High, excellent tensile strength. | High (Base steel strength plus zinc protection). |
| Typical Applications | Water, oil, gas, general industrial piping. | Chemical, pharmaceutical, food & beverage, marine. | Outdoor piping, residential water supply, non-potable water. |
The selection process also involves considering the long-term total cost of ownership, which includes not just the initial purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential replacement costs. A higher upfront investment in a stainless steel elbow may result in significant savings over its lifespan in corrosive environments, due to reduced maintenance and extended operational periods. Conversely, for non-corrosive applications, a galvanized steel elbow can offer a cost-effective solution with adequate rust protection for many years. Reputable manufacturers provide detailed material certifications and technical support to assist clients in making these critical decisions.

Recognizing that off-the-shelf solutions may not always meet the unique demands of every project, leading manufacturers of steel elbow products offer extensive customization options. This includes specific material grades, non-standard dimensions, unique bend radii (e.g., 3D, 5D, 7D, 10D elbows), specialized coatings, and various end preparations. Custom solutions are particularly valuable in complex industrial projects where space is limited, flow dynamics are critical, or specific chemical resistances are required. Engaging with a manufacturer that possesses deep engineering expertise and flexible production capabilities ensures that even the most challenging design specifications can be met with precision and reliability. This collaborative approach enhances project efficiency and reduces potential costly modifications down the line.

Trustworthiness in the B2B sector is built upon consistent quality, transparent processes, and robust customer support. Reputable steel elbow suppliers typically hold multiple international certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, demonstrating their adherence to globally recognized best practices. They also provide comprehensive warranties for their products, assuring clients of their commitment to durability and performance. Furthermore, reliable delivery schedules, often expedited for urgent requirements, and responsive customer service teams that offer technical assistance, order tracking, and after-sales support are hallmarks of a trustworthy partner. For instance, Lion Pipeline, with over 15 years of experience in pipeline solutions, consistently delivers fittings that meet stringent industry standards, ensuring peace of mind for their global clientele.
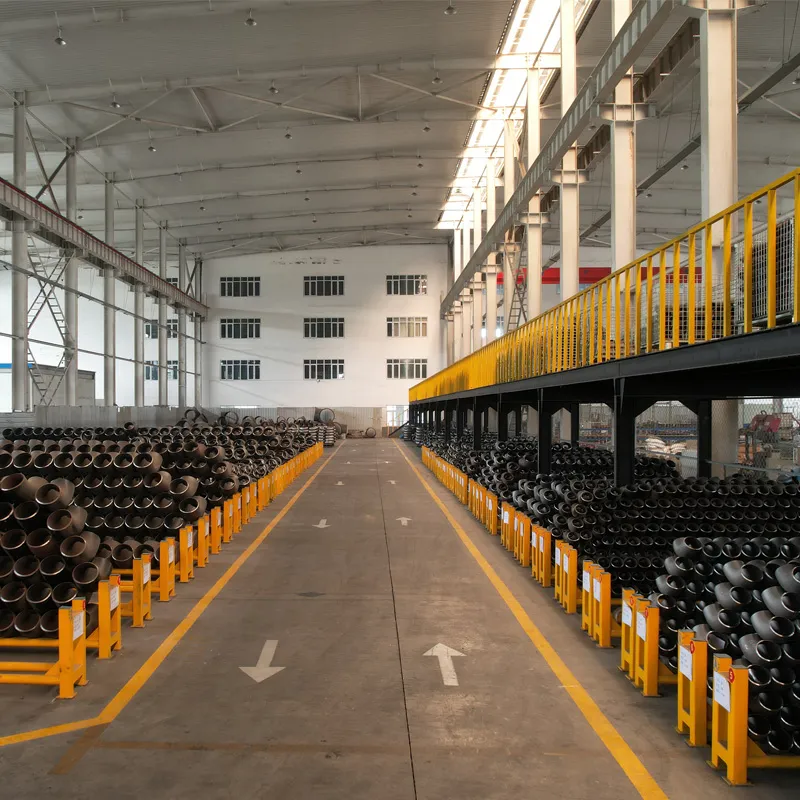

Choosing the right supplier for steel elbow fittings means selecting a partner dedicated to product excellence, comprehensive support, and transparent operations. It’s an investment in the long-term reliability and efficiency of your industrial pipeline systems.
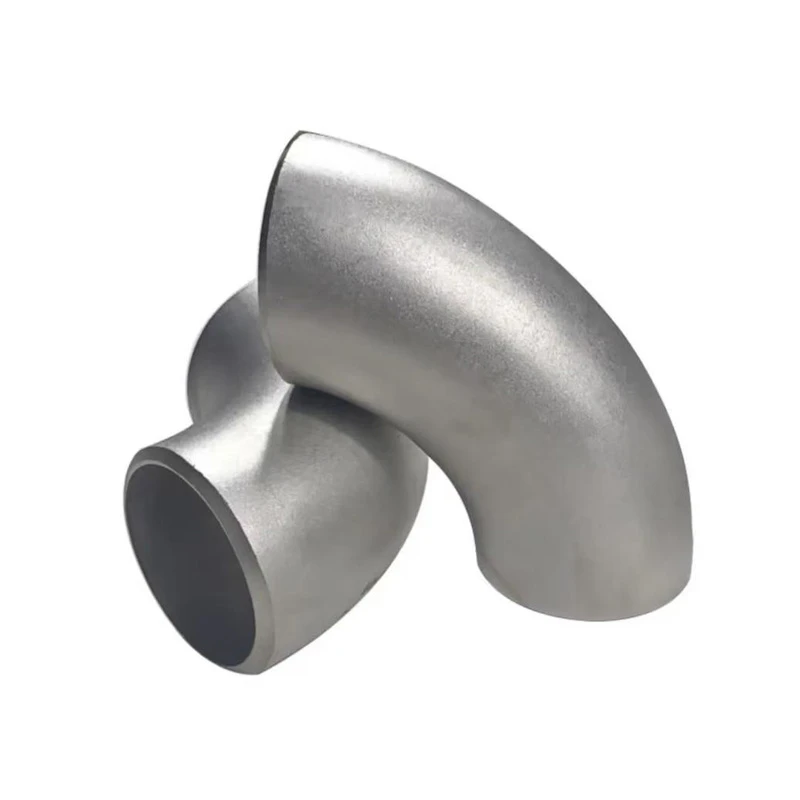



Where to Buy Stainless Steel Pipes and Tubing for Sale Together
The Future of Smart Flange Technology
Tee Pipe Fitting in Industrial Process Piping
Prefabricated Pipe in Shipbuilding Applications
How Anti Corrosion Pipe Extends Pipeline Lifespan
Cts Pipe Fittings for Potable Water Systems
If you are interested in our products, you can choose to leave your information here, and we will be in touch with you shortly.